An aneurysm is a swelling or dilatation in a blood vessel. Aneurysms can occur in any blood vessel, but are much more common in arteries, although they do occur rarely in veins. An abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a dilatation in the abdominal (tummy) part of a major artery - the aorta. This is one of the commonest types of aneurysm.
Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) is the term used to describe stent repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. This is the modern minimally invasive method of repair. It is the preferred method in this practice, and is used to treat 90% of our patients with AAA. The stent is introduced through small incisions in the groin. It is assembled within the AAA.
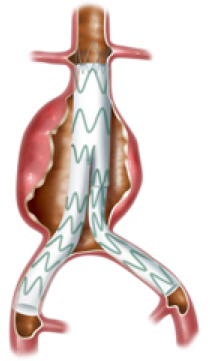 In healthy people the aorta is usually about 2.0-2.5 cms (20-25mm) in diameter although this can vary with age and gender. An aneurysm greater than 5.0 cms across requires scans every 3 months although there is some variation in recommendations. When an aneurysm reaches 5.5 cms most surgeons would consider offering surgical intervention. This is because, at this size, the aneurysm has a greater risk of rupture. It then becomes as safe to have an operation to repair the aneurysm, as it is to leave the aneurysm alone.
In healthy people the aorta is usually about 2.0-2.5 cms (20-25mm) in diameter although this can vary with age and gender. An aneurysm greater than 5.0 cms across requires scans every 3 months although there is some variation in recommendations. When an aneurysm reaches 5.5 cms most surgeons would consider offering surgical intervention. This is because, at this size, the aneurysm has a greater risk of rupture. It then becomes as safe to have an operation to repair the aneurysm, as it is to leave the aneurysm alone.
Surgery may also be considered if your aneurysm is rapidly expanding on regular scans or it starts to cause other complications. Endovascular treatment of aneurysms has lower operative mortality than open surgery and it was proposed that treating smaller aneurysms with endovascular stents would lead to better outcomes.
To reduce the risk of DVT - Anti-embolic graduated compression stockings may be used, providing there is no evidence of hardening of the arteries in the legs. Intermittent compression of the legs and/or feet using airbags is sometimes used in theatre to improve blood flow in the leg veins during the anaesthetic. Most patients also receive heparin injections to reduce the risk of blood clots forming. After your operation you will be encouraged to move around as early as possible.
To reduce the risk of infection - Antibiotics will be given at the start of the operation and sometimes for one or two doses after the operation. Physiotherapy will be started shortly after the operation to prevent secretions accumulating in the chest.